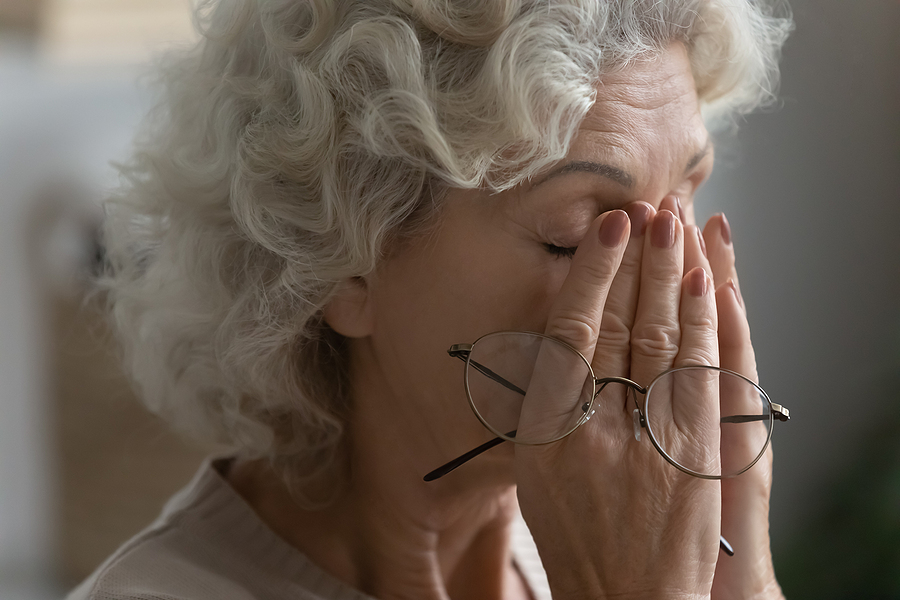
Giant cell arteritis is an inflammation of the lining of medium-to-large arteries. Since this condition most often affects arteries in the head, especially near the temples, it is sometimes called temporal arteritis. Although the cause is unknown, doctors think it might be due in part to a faulty immune response. Some links to certain infections or genes have also been established. Patients over 50 are the most commonly affected, especially if they also suffer from polymyalgia rheumatica, another inflammatory disorder.
Symptoms of Giant Cell Arteritis
With giant cell arteritis, inflamed and swollen blood vessels become tender and can eventually suffer damage. Since the affected blood vessels usually supply blood to the head and neck, the most frequent symptoms include:
- Throbbing headaches, especially if this is a new symptom
- Scalp tenderness
- Jaw pain, especially when chewing or opening the mouth wide
- Sudden vision changes – blurred vision, double vision, or vision loss
- Fever
- Excessive fatigue
When giant cell arteritis affects blood vessels in other areas of the body, you might notice other symptoms, including:
- Arm pain
- Muscle aches
- Weakness
People with both polymyalgia rheumatica and GCA might also have pain and/or stiffness in the neck, upper arms, shoulder, or hips.
When to See a Doctor
If you are experiencing a new, persistent headache, especially in conjunction with any of the other symptoms listed above, it’s important to see a doctor as soon as possible. Although symptoms can go away temporarily, be intermittent, or only gradually get worse, leaving giant cell arteritis untreated can result in permanent vision loss. Vision problems might begin suddenly, even if you experience other symptoms first.
Diagnosis
A doctor will conduct a thorough physical examination, paying special attention to your head. A sensitive scalp or a thick artery on the side of your head that is tender to the touch might be present to help with diagnosis. Other tests and procedures might be required such as blood tests, liver function tests, MRI, or a biopsy of the temporal artery.
Treatment Options
Treatment usually consists of corticosteroid medications like prednisone given orally. Most patients find relief from symptoms within days of beginning treatment. Starting treatment quickly is especially important with giant cell arteritis because it can sometimes prevent permanent vision loss. Even if your symptoms subside with medication, though, relapses can occur. You will most likely need to continue treatment for a year or two, with regular follow-up and check- ups.
Worried About Giant Cell Arteritis? We’re Here to Help.
The team at Advanced Rheumatology of Houston has the necessary experience to diagnose and treat giant cell arteritis quickly and effectively. If you are having symptoms, especially changes to your vision or a new or prolonged headache, give us a call at (281) 766-7886 to schedule an appointment today. Our compassionate specialists are ready to work with you to develop an appropriate treatment plan and guide you through the process of any ongoing and follow-up care you might need.