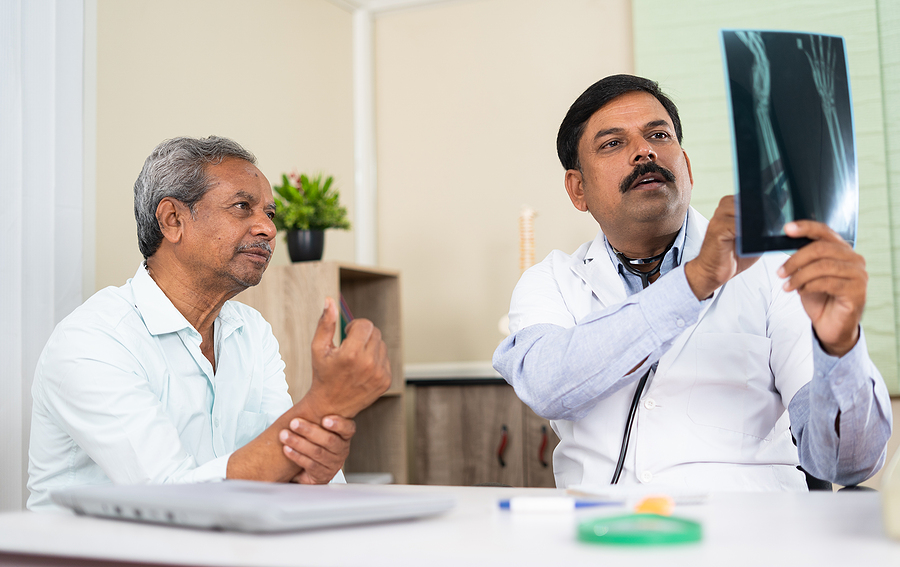
You may first start to feel pain and stiffness in your joints, or your fingers begin to swell. At that point, you may be tempted to pass it off as just another sign of getting older.
However, aches and pains do not have to be a by-product of aging. You do have options.
What Are Rheumatic Diseases?
Rheumatic disease is an umbrella term for a group of disorders that cause pain and mobility issues. They are typically characterized by inflammation that affects the joints, tendons, ligaments, bones, and muscles.
Some common types of rheumatic diseases include:
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system attacks healthy tissue, typically in the joints of the hands and feet.
- Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common type of arthritis that occurs when the cushioning cartilage at the ends of your bones begins to wear down.
- Lupus is another disease where the immune system attacks healthy tissue and organs. It can damage several parts of the body, including the kidneys, joints, lungs, heart, blood vessels, skin, and brain.
- Gout is a type of arthritis caused by excess uric acid in the bloodstream, which crystallizes and gets deposited in the joints. It is usually characterized by sudden pain, swelling, and redness in the big toe.
- Spondyloarthropathies refers to a group of diseases that cause arthritis in the spine surrounding joints.
What Are the Signs?
While the signs and symptoms of rheumatic diseases can vary and attack different body parts, depending on the specific disease, there are some common symptoms associated with these conditions, such as:
- Joint pain
- Stiffness when you wake up or after periods of inactivity
- Swelling in the joints and limited range of motion
- Affected joints are red and warm to the touch
- General fatigue
- Possible low-grade fever
- Unintentional weight loss
- Some diseases, such as lupus, can cause skin rashes
How Are Rheumatic Diseases Detected?
To diagnose a rheumatic disease, a healthcare provider will do the following:
- Ask about personal and family medical history, symptoms you’ve been experiencing, and their duration.
- Examine your joints for signs of inflammation, such as swelling, redness, and warmth.
- Order laboratory tests to help identify inflammation and autoantibodies often present in rheumatic diseases.
- Request tests such as X-rays, ultrasounds, and MRIs to view detailed images of your joints or tissues
Unfortunately, there is no cure for rheumatic diseases. However, early detection is crucial for several reasons:
- Access to appropriate treatments to help control symptoms and slow the progression of the disease
- Prevent irreversible joint damage
- Improved prognosis
- Reduced risk of complications
- Enhanced quality of life
Our staff at Advanced Rheumatology of Houston understands that early detection is essential for managing a rheumatic disease. We are dedicated to helping our patients find relief through a customized treatment plan, which typically includes medications, therapy, and lifestyle changes. We also participate in various research studies to ensure we are always on the cutting edge of innovative treatments.
Contact us to schedule an appointment by calling (281) 766-7886.