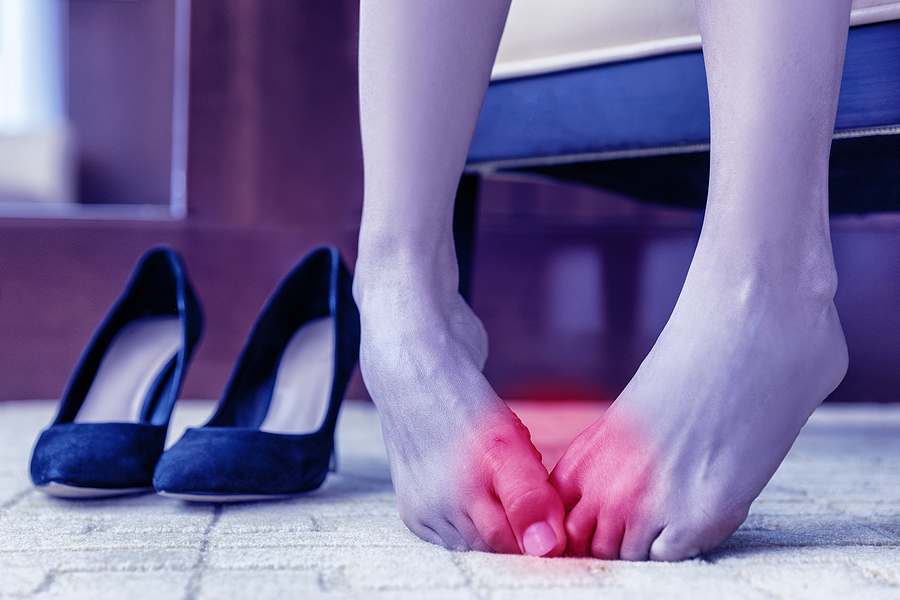
Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by sudden and severe attacks of pain, swelling, and redness in the joints, often affecting the big toe. In this article, we’ll discuss the causes, symptoms, signs, and treatment options for gout.
We’ll explain the factors that contribute to its development, the telltale signs of an impending flare-up, and the various medical interventions and lifestyle changes that can help manage and prevent this painful condition.
What Causes Gout?
Gout is primarily caused by the accumulation of urate crystals in the joints, leading to inflammation and pain. This occurs when there’s an excess of uric acid in the blood, a condition known as hyperuricemia.
Uric acid is a byproduct of the breakdown of purines, substances found in certain foods and naturally produced by the body. Factors such as:
- Genetics
- A diet high in purine-rich foods like red meat and seafood
- Excessive alcohol consumption, and
- Certain medical conditions
can all contribute to elevated uric acid levels, triggering the onset of gout.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Gout?
The signs and symptoms of gout typically manifest as sudden and intense joint pain, most commonly in the big toe, but it can affect almost any joint. This pain is often accompanied by swelling, redness, and warmth in the joint.
Gout attacks can occur unexpectedly, often waking you up from sleep with excruciating discomfort. Other common symptoms include joint stiffness, limited range of motion, and the presence of tophi, which are urate crystal deposits that may form lumps under the skin.
Can Gout be Prevented?
If you’ve had gout previously, there are certain lifestyle changes and strategies you can implement to prevent a flare-up. Your main goal is to reduce the risk of uric acid accumulation and subsequent crystal formation. Start by:
- Maintaining a balanced diet low in purine-rich foods
- Moderating your alcohol consumption
- Staying hydrated to help flush out excess uric acid
- Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise
Medications that lower uric acid levels may also be prescribed if you experience recurrent flare-ups.
How is Gout Treated?
Gout treatment aims to reduce pain and inflammation and prevent future flare-ups. Medications like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), colchicine, and corticosteroids are commonly prescribed during gout attacks. Certain medications like allopurinol or febuxostat may also be recommended to lower uric acid levels in the blood and prevent crystal accumulation.
For most patients, the prevention methods listed above are also incorporated into a treatment plan. A comprehensive approach that combines both medication and lifestyle adjustments is generally the best approach to treating and managing gout.
Contact Us Today to Schedule an Appointment
At Advanced Rheumatology of Houston, we know how painful gout can be. That’s why we offer same-day gout appointments, to provide you with much-needed relief from painful gout symptoms.
As well as treating your symptoms, we can help you come up with a plan to manage your gout. With regular appointments and a rheumatologist who understands your needs, you’re in the best position to keep your gout at bay.
Schedule your appointment here to find safe, effective relief from your gout.