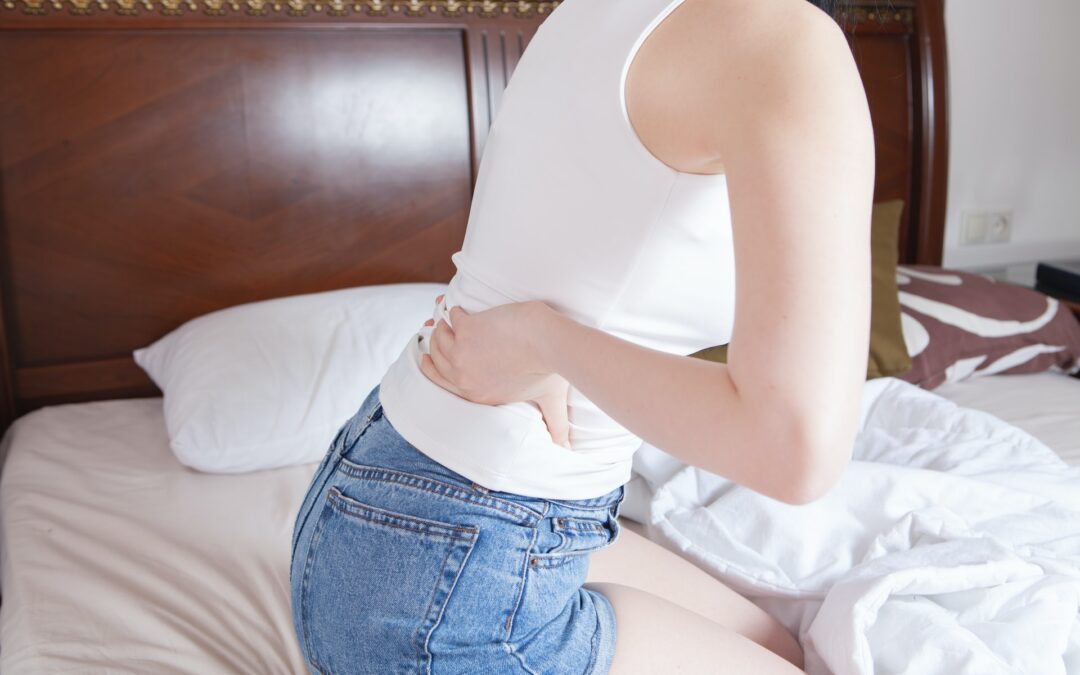
Spondyloarthritis isn’t just one type of arthritis. Instead, it refers to a group of inflammatory diseases that mainly affect the spine and pelvis. However, it can also impact limbs and the end of bones where the tendons and ligaments attach.
This blog post will discuss potential causes of spondyloarthritis and the treatment options available for anyone living with this disease.
Risk Factors
Spondyloarthritis targets both males and females in their late teens to early adulthood. The exact cause is unknown, but it is thought to be genetic. Studies have shown that people with the HLA-B27 gene are more likely to develop spondyloarthritis. However, having the HLA-B27 gene doesn’t necessarily mean a person will eventually get the disease – something else typically needs to occur to trigger it. Many theories suggest infection or an imbalance of the gut microbiome as common triggers.
Diagnosing Spondyloarthritis
Symptoms can vary from mild to severe and may include pain, stiffness, and inflammation in the affected joints. In some cases, spondyloarthritis can also cause fatigue, weight loss, and fever.
The type of spondyloarthritis determines where symptoms might occur, such as:
- Ankylosing spondylitis, the most common type, is indicated by pain in the lower back and buttocks.
- Enteropathic arthritis is typically accompanied by inflammatory bowel disease.
- Psoriatic arthritis is associated with the skin disease psoriasis. Along with pain in the spine, you may also experience neck soreness.
- Reactive arthritis may begin with a urinary tract or intestinal infection. It may also cause conjunctivitis (pink eye).
Your healthcare provider will conduct a physical exam and discuss your medical history. They will likely order X-rays of the spine and pelvis and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). A blood test will check for the HLA-B27 gene to help confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options
There is no cure for spondyloarthritis, but treatment can help to relieve symptoms and prevent further damage to the joints. Common treatments include medications such as NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and DMARDs to help reduce inflammation and pain. Tumor necrosis (TNF) alpha-blockers are biologic agents that are very effective in treating certain types of arthritis in the spine.
Physical therapy can also help reduce pain and improve mobility. Exercise is essential for maintaining joint function and supporting overall health. Swimming is an excellent low-impact exercise for people with spondyloarthritis.
Surgery is typically only recommended when other treatments have failed to provide relief.
Living with Spondyloarthritis
Early diagnosis of spondyloarthritis leads to the best treatment outcomes. If you live in Houston or the surrounding area, Advanced Rheumatology of Houston can help. We specialize in treating rheumatological conditions and other autoimmune diseases, including spondyloarthritis, scleroderma, and lupus.
If you are experiencing any of the symptoms of spondyloarthritis, please contact us to schedule an appointment with one of our specialists. Fill out our contact form or call us at (281) 766-7886. We will work with you to create a treatment plan that helps you live your best life.