Vasculitis is not a specific disease; rather, the term refers to a group of rare diseases that cause inflammation of blood vessels, including arteries and veins. Inflammation of blood vessels can eventually lead to a thickening of the blood vessel walls, which reduces the width of the blood vessel passage itself, restricting blood flow. Unfortunately, vasculitis can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender, but, fortunately, most types are rare. Some types are restricted to a particular age group, such as Kawasaki’s disease, which only affects children, and giant cell arteritis, which is found only in adults over the age of 50. If you are or think you may be living with vasculitis, read on to learn more about its effects on the body and available treatment options.
Causes of Vasculitis
Generally speaking, the causes of vasculitis are unknown, although genetic factors do seem to play an important role. Vasculitis is thought to be an autoimmune issue where the body, specifically the blood vessels, come under attack from your own immune system. Some cases of vasculitis are caused by a reaction to medicine. Vasculitis can also occur as a result of other rheumatic diseases like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis.
Diagnosis of Vasculitis
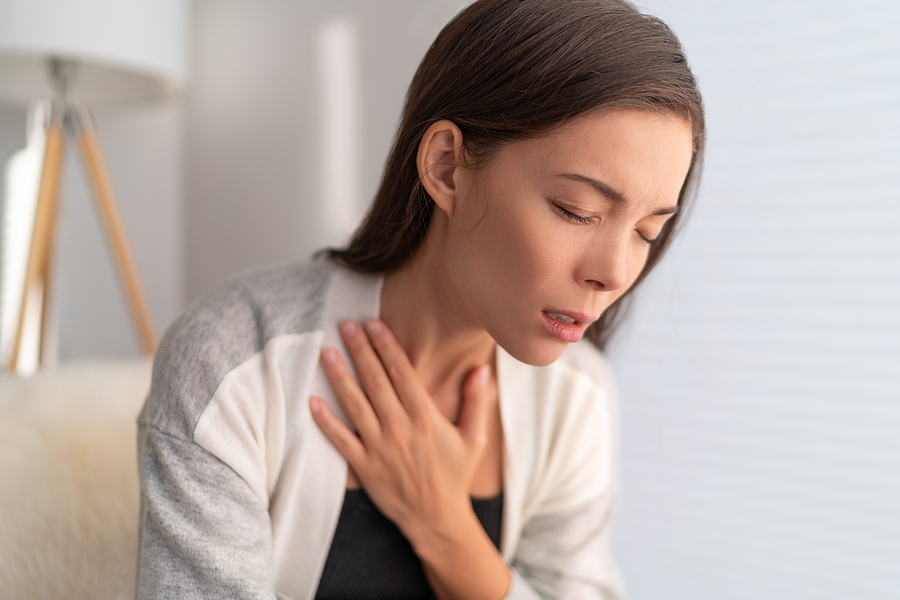
Since vasculitis can restrict blood flow to various organs and tissues throughout the body like lungs, nerves, and skin, there is a wide range of symptoms possible, including shortness of breath and cough, numbness or weakness in hands or feet, or skin issues like red spots, lumps, or ulcers. Diagnostic tests and procedures will likely be needed to rule out other conditions that can sometimes mimic vasculitis. Doctors generally use blood tests, imaging tests, including x-rays of blood vessels, or biopsies to help detect the type of vasculitis based on the size of the affected blood vessels and organs involved.
The Effects of Vasculitis on the Body
Vasculitis that affects small blood vessels often results in those small vessels breaking, creating tiny areas of bleeding in the tissue. These areas then appear as small red or purple dots on the skin. When larger blood vessels are involved, the inflammation may cause swelling or even produce a nodule or ulcer on the skin. Sometimes the inside of a blood vessel may narrow and close completely due to a blood clot. Reduced, restricted, or lack of blood flow to tissues can eventually cause the tissues to die.
Treatment Options
Although vasculitis can be mild and limited to a single episode, it is important to talk to a doctor to determine the type, extent, and possible treatment since reduced blood flow can have serious, long-lasting consequences on your body. Most treatments focus on reducing the inflammation and preventing additional flare-ups, making living with vasculitis more comfortable.
Common treatments for vasculitis include:
- Glucocorticoids, or steroids like prednisone, which help reduce inflammation
- Immune-suppressing drugs, which have fewer side effects than steroids for long-term use
- Surgery to repair blood vessels
Living with Vasculitis? We can help.
At Advanced Rheumatology of Houston, we have dedicated doctors ready to discuss your symptoms and diagnose your specific vasculitis issues. Our team of compassionate specialists understands that each patient’s needs are different, and we stand ready to work with you to determine the most appropriate treatment and health management plan to help provide you with both the pain relief and quality of life that you are hoping for. Please call us today at (281) 766-7886 to schedule an appointment.